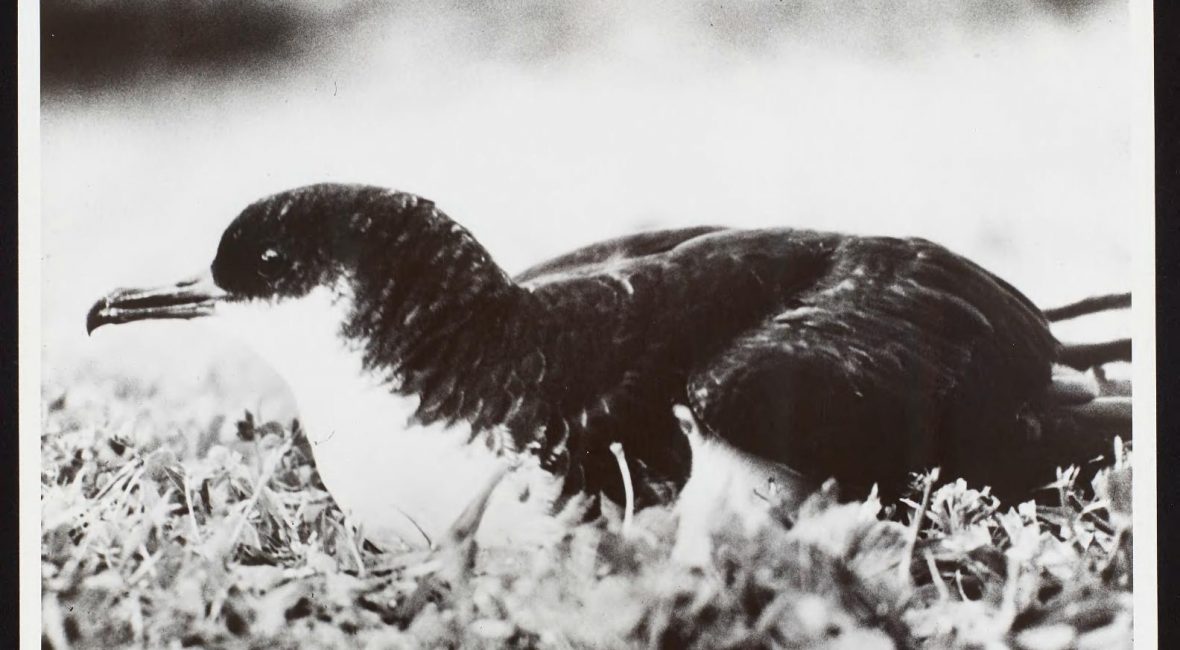
In the middle of the Cold War, the Smithsonian Institution embarked on the Pacific Ocean Biological Survey Program (POBSP) to survey U.S. territory islands and atolls dotting the central Pacific Ocean. From 1963 to 1969, researchers sought to inventory the plants and animals present on the islands, observe seasonal variations in numbers and reproduction, and the distribution of pelagic birds. Over the course of the survey, researchers observed approximately 150,000 pelagic birds at sea, banded 1,800,000 birds, and surveyed the flora and fauna of the islands, the most comprehensive study at the time. An incredible amount of data was collected during the POBSP, drastically increasing information available about the ecology of the small islands.
Continue reading